Russian Physicists Determine Indices Enabling Prediction of Laser Behaviour
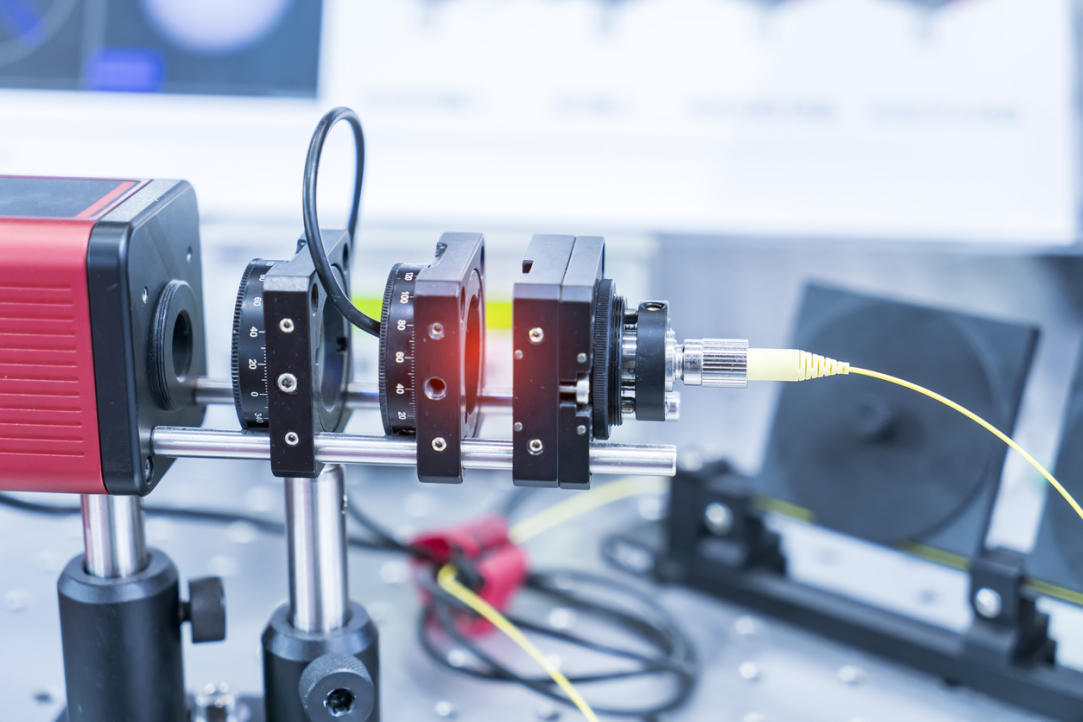
Russian scientists, including researchers at HSE University, examined the features of fibre laser generation and identified universal critical indices for calculating their characteristics and operating regimes. The study findings will help predict and optimise laser parameters for high-speed communication systems, spectroscopy, and other areas of optical technology. The paper has been published in Optics & Laser Technology.
Erbium fibre lasers are devices that generate light within a fibre doped with ions of the rare-earth element erbium. These lasers operate at a wavelength of approximately 1.5 micrometres, making them ideal for long-distance data transmission with minimal loss. Radiation at other wavelengths requires amplification every 20-30 kilometres when passing through optical fibre, whereas radiation from erbium lasers needs 2-3 times fewer amplifiers, significantly reducing equipment and operational costs. Moreover, erbium lasers can produce radiation with a narrow spectral linewidth (less than 1 kHz), which is used in high-precision optical sensors and transducers.
As demands for data transmission speed and capacity increase, there is a growing need to miniaturise lasers and shorten cavities without compromising their efficiency. A cavity is a component of a laser that consists of two mirrors and is responsible for amplifying light as it passes repeatedly through an active medium.
Depending on the cavity length and the concentration of erbium ions, the laser can operate in different regimes — either pulsed or continuous-wave (CW). The primary challenge is that reducing the size of the cavity requires an increase in the concentration of erbium ions. This causes the laser to operate in pulsed mode, which can result in data transmission instability, power limitations, and increased noise levels.
A group of Russian scientists, including physicists at HSE University, prepared two types of active fibres for seven lasers and compared the effects of erbium ion concentrations (ranging from 0.03% to 0.3%) on the laser parameters. As a result, they determined the parameters of the active medium and pump power that allow for a short cavity length and CW operation simultaneously, as well as the conditions under which the switching from CW to pulsed mode occurs.
'The transition from continuous-wave to pulsed operation regime is somewhat analogous to a classical phase transition, which follows mathematical laws and characterises processes in other systems, such as liquids and solids. Lasers with a high concentration of erbium ions exhibit two thresholds: the first is associated with the onset of pulsed mode operation, while the second marks the transition to continuous-wave mode. These laws resemble power-law dependencies and describe how the laser parameters change near the generation threshold,' explains Oleg Butov, co-author of the paper, Deputy Director and Head of the Laboratory of Fiber Optic Technologies at Kotelnikov Institute of Radioengineering and Electronics of RAS.
For the first time, researchers experimentally determined the critical indices for erbium lasers—specifically, the slopes of the logarithmic relationships between the frequency, duration, and amplitude of laser pulses and the laser radiation power.
'We have established that the calculated dependencies are universal for erbium lasers, regardless of significant variations in the core composition of the active fibre, cavity length, and Q-factor (a ratio of stored energy to energy consumed in one period). The results will enable predictions of the erbium fibre lasers radiation parameters and facilitate the optimisation of their operation for various applications,' according to Alexander Smirnov, co-author of the paper and Professor at the ‘Nanoelectronics and Photonics’ Joint Department with Kotelnikov Institute of Radioengineering and Electronics (RAS) of the HSE Faculty of Physics.
The study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (No. 20-72-10057).
See also:
Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
Scientists Uncover Why Consumers Are Reluctant to Pay for Sugar-Free Products
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how 'sugar-free' labelling affects consumers’ willingness to pay for such products. It was found that the label has little impact on the products’ appeal due to a trade-off between sweetness and healthiness: on the one hand, the label can deter consumers by implying an inferior taste, while on the other, it signals potential health benefits. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
'Even among Geniuses, Luck Plays a Role in Winning a Nobel Prize'
Denis Bodrov studies particle physics and works at one of the four electron–positron colliders in the world. In this interview with the HSE Young Scientists project, he talks about his efforts to go beyond the Standard Model, discusses tau leptons, and shares his affection for Moscow.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.